Fast casual restaurants- dejunking fast food for urban consumers
Fast casual restaurants capture consumer demand for both high-quality food and quick service, combining the qualities that attract diners to fast food chains as well as to their casual dining counterparts. The fast casual industry has been gaining popularity and experiencing remarkable growth, especially in the US. EIC sees the fast casual business model as a strategy for distinguishing restaurants in the face of fierce competition in the Thai restaurant industry. Success factors for this type of business establishment are the ability to differentiate, the capacity to efficiently manage inventories, maintaining food safety, and the adoption of technology to give customers novel dining experiences.
Author: Puripat Sophonkeereerat

|
Highlight
|
Fast casual restaurants cater to today’s diners who demand high-quality food while also wanting convenience and fast service. The fast casual genre combines the key features of fast food establishments and casual dining restaurants. It emphasizes speed of service like fast food restaurants but serves higher-quality food, using fresh ingredients and avoiding frozen or processed products. Fast-casual restaurants usually cook food to order in an open kitchen. Another key feature of a fast casual establishment is moderate prices comparable to fast food chains. For example, a burger from Shake Shack, a famous US fast casual brand, costs USD 5.29, only slightly higher than a USD 3.99 McDonald's burger. The quality of Shake Shack food is closer to that of casual dining places like Applebee’s and T.G.I. Friday whose meals cost much more.
The fast casual sector has gobbled up a bigger slice of the market despite intense competition in the restaurant industry, leading many businesses to face revenue losses. Especially in the US, big fast food franchises like McDonald's experienced declining revenue while fast casual chains like Shake Shack grew on average by 48% annually during 2014-2016. Shake Shack started as a small food cart in Madison Square Park, growing into a 129-location burger chain at present. The selling point for Shake Shack is the use of good ingredients such as 100% all-natural Angus beef, raised with neither hormones nor antibiotics. Panera Bread, a premium bakery-cafe chain, is another front runner in the fast casual sector with more than 2,000 locations. Its sale increased on average by 13% annually during 2006-2016, leading to total sales in 2016 of around USD 2.8 billion. The key success factors for Panera Bread are its diverse menu and the brand’s ability to ride the wellness wave with gluten-free and low-fat items. Moreover, foodies who are watching their weight can choose to order half a portion or change to a thinner type of bread.
Fast casual restaurants in Thailand are currently not as prevalent but could be the answer to the increasing demand for dining out, speedy food service, and healthier meal options. Currently not many chains identify as fast casual. The few that do include Pepper Lunch, Au Bon Pain, and MOS burger. EIC conducted a survey and found that 30% of Thais are willing to pay more to dine out, reflecting a consumer preference for convenience while still valuing meal times. We further found that 40% of the respondents are concerned with health over other issues like income and jobs as they age. More than 90% of the respondents expressed willingness to pay more for higher-quality products. These consumer trends give fast casual businesses an opportunity to deliver both convenience and food quality to take advantage of these trends.
The key to sustaining the success of a fast casual establishment is to differentiate a brand from its competitors. The restaurant industry is full of competitors and has low entry barriers. Thus, an important strategy for a restaurant is to separate itself from the rest of the market with a unique menu or atmosphere. Most fast casual businesses will let their customers substitute ingredients or change portion sizes. This model is consistent with the EIC’s survey findings that 79% of respondents will pay more if goods can be customized. Fast casual places are also designed to evoke a feeling of comfort and convenience.
The ability to efficiently manage ingredients and uphold food safety standards is another essential component. Many fast casual brands obtain their ingredients from local sources to ensure freshness and familiarity of flavors for customers. Maintaining food safety standards is also crucial since one oversight can lead to harsh repercussions for the brand’s image, as in the case of Chipotle Mexican Grill, a chain that became successful with a fast casual model but that faced food safety issues during the latter half of 2015. The incidents decreased consumers’ confidence in the brand and led sales volume to decelerate in 2015 and suffer negative growth in 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 1: Price of a fast casual meal is comparable to that of a fast food meal and much lower than that of a casual dining dish.
Unit: USD
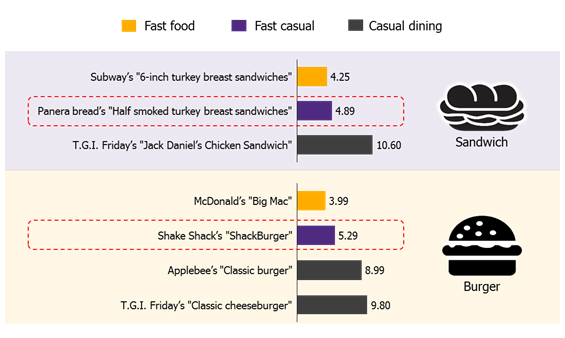
Source: EIC analysis based on data from companies and Fast Food Menu Prices
Figure 2: Thai consumers are willing to pay more for quality and customizable goods.
Unit: % of survey respondents
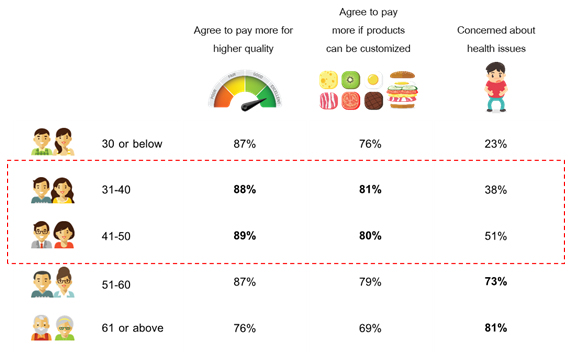
Source: EIC analysis based on data from EIC survey (February 2017)